Network Topology
Local Area Network (LAN) Layout
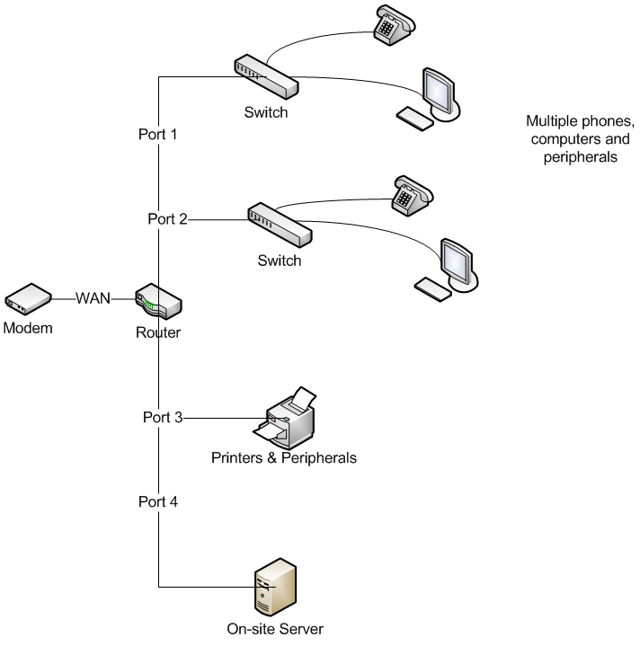
The LAN is everything in your network starting from the Internet connection. In most cases this will be from the modem inward. It can include the router, switches and computers. How these devices are networked can affect the connectivity of your VoIP telephones and computers. Looking at the devices and how they are connected can often lead to solving some issues, including one-way audio and lost connections.
Using multiple routers
Having multiple routers on your network is often problematic for VoIP (and can result in you being unable to receive a phone call). There are various reasons for this, but to summarize, routers do many jobs. Some of these jobs can have an explicit impact on VoIP traffic in particular. The more routers, the more likely one of them will affect your VoIP system. For this reason, we recommend using a single router whenever possible and configuring QoS rules to further prioritize voice traffic.
Modem/router combinations
It is not uncommon for a DSL or cable provider to use a modem with a router built in. If you have your own router as well, this may cause problems. As a solution, the modem/router combination can often have the router portion disabled. This is called “bridging.” You would need to contact your internet service provider (ISP) to do this. Please also be aware that often times these modem/router combination devices are for home internet use and cannot handle the increased traffic of a business environment.
Firewall Configuration
Most routers include a firewall, which is a filter that blocks traffic that should not be allowed in or out. For smaller offices with off-the-shelf routers, these firewalls may need to be modified or turned off. On enterprise level equipment, certain rules may need to be added to allow RingByName’s traffic to flow through. Technicians can assist your IT administrator in making any necessary adjustments. However, if you have a complex setup that is necessary for security reasons, you may need to have a network administrator on-site to set up the phones using static IPs and static ports in your firewalls.
For RingByName to work properly, the following ports need to be opened:
- 5060 to 5090 TCP
- 10,000 to 30,000 UDP
Equipment to Avoid
- Wireless and Satellite Internet Providers: these are a source of problems when using a VoIP service. Because of the way the Internet signal is delivered to your office, wireless-only and satellite internet connections can result in dropped calls and sound quality issues.
- Wireless Adapters: these can create problems because your voice is real time; anything that may slow down the VoIP traffic can cause noticeable call quality issues. Connecting the phones to your Internet connection via a wireless adapter is not recommended. You should avoid using these methods to ensure the highest quality calls.
The Ideal Network
An ideal network is crucial for the functionality of the phone. Achieving an ideal environment is simple once you know the terminology. In an everyday network, you will only need to work with a few pieces of equipment connected in the right order. Often this equipment looks the same and can be a hard to recognize.
- Modem: The modem connects you to the Internet. DSL providers often use modems with a router built in. These modem/router combinations are not always up to the task of handling VoIP traffic and may require changes.
- Router: The router is crucial for VoIP phone service. It creates a private network for all connected devices, helping you to share the internet and, at the same time, providing security features. Please Note: You cannot have two routers on your network. If you do, your VoIP phones will be unable to communicate correctly (even if your computer can).
- Switch: You can use a switch to create additional ports to your router. However, your switch must be plugged into a router in order to work correctly.
